Linqing Luo and Prof. Kenichi Soga from our group recently published a paper in Journal of Lightwave Technology.
Y. Mei, X. Xu, L. Luo and K. Soga, “Reconstruction of Distributed Strain Profile Using a Weighted Spectrum Decomposition Algorithm for Brillouin Scattering Based Fiber Optic Sensor,” in Journal of Lightwave Technology, vol. 38, no. 22, pp. 6385-6392, 15 Nov.15, 2020, doi: 10.1109/JLT.2020.3011686.
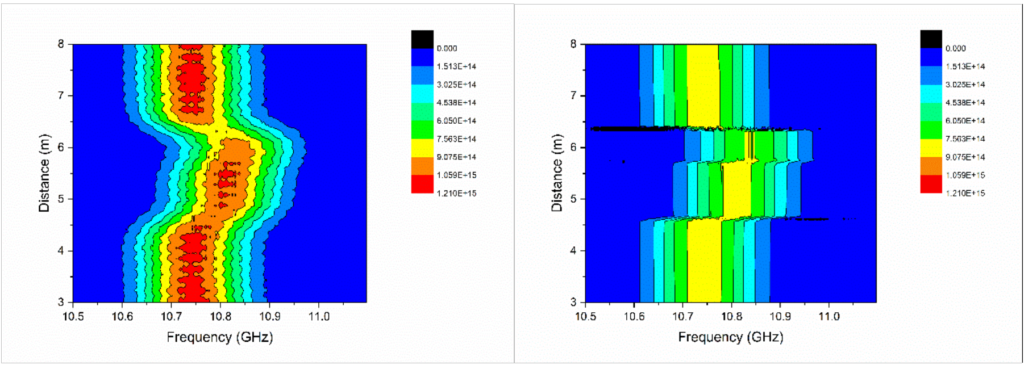
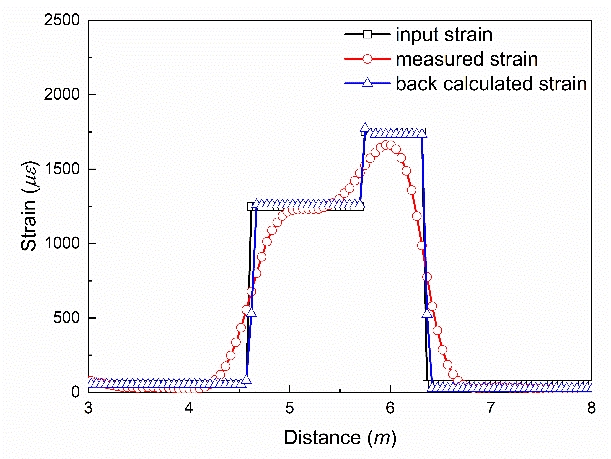
Brillouin scattering based fiber optic strain sensor is used to measure distributed strain profile of a structure for structural health monitoring. A distributed strain profile is derived from the Brillouin spectrum peaks but error is induced when a local strain change occurs in a distance scale smaller than the spatial resolution. In this study, a new algorithm is proposed to reconstruct a Brillouin spectrum by eliminating low qualified data from the raw spectrum data. This is achieved by evaluating the strain gradient profile and statistically decomposing the power, width, and peak frequency of the raw spectrum data. This algorithm is versatile because it can be applied to various strain shapes and magnitudes. The reliability of the algorithm is verified experimentally by showing that the error of the strain profile obtained using the new method becomes 25% of that using the conventional peak detection method.
Figure 1. Measured Brillouin scattering spectrum (left) and back analyzed Brillouin scattering spectrum (right)
Figure 2. Measured and reconstructed strain using the back-analysis method with a connected step shape input strain